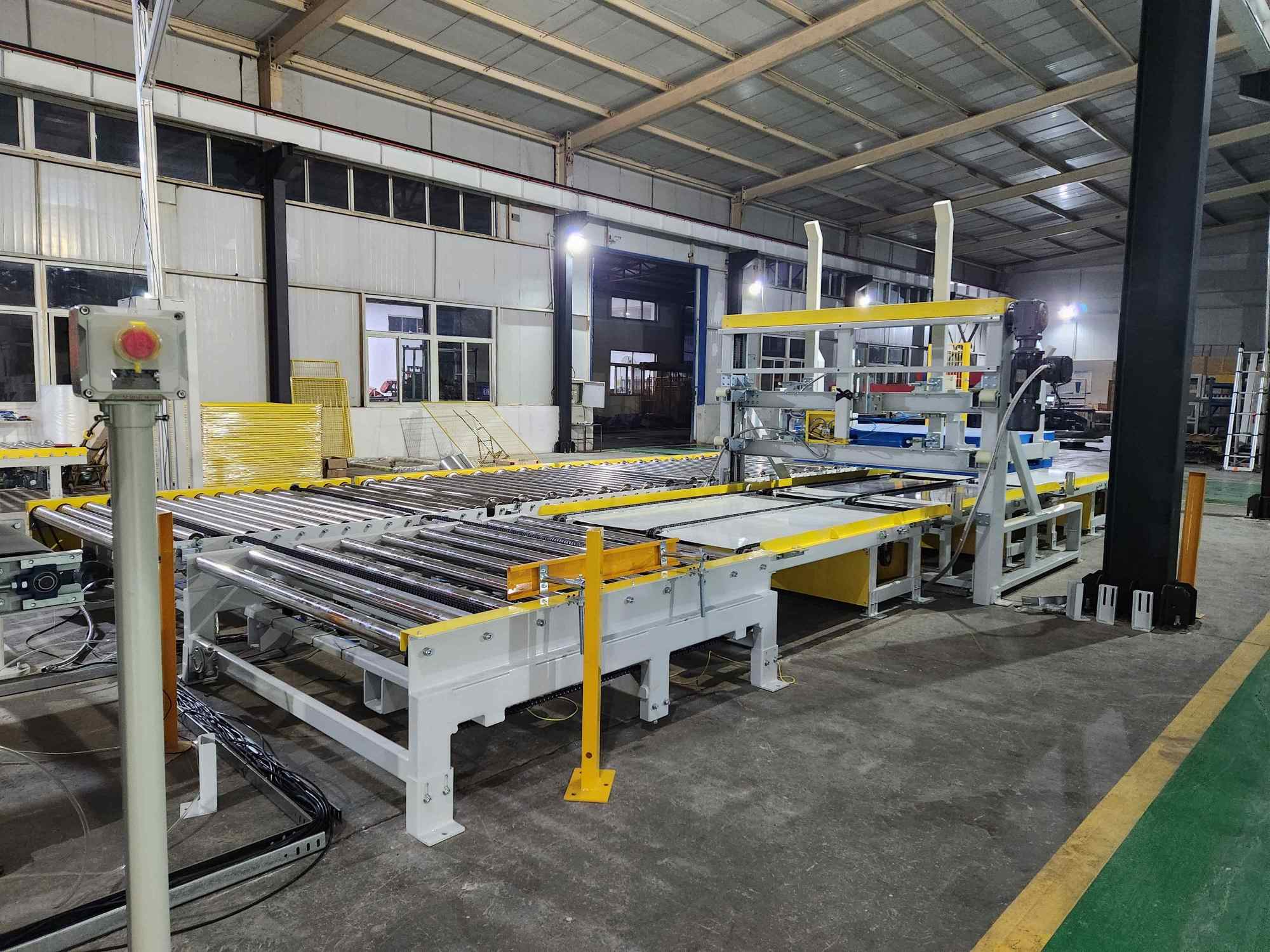
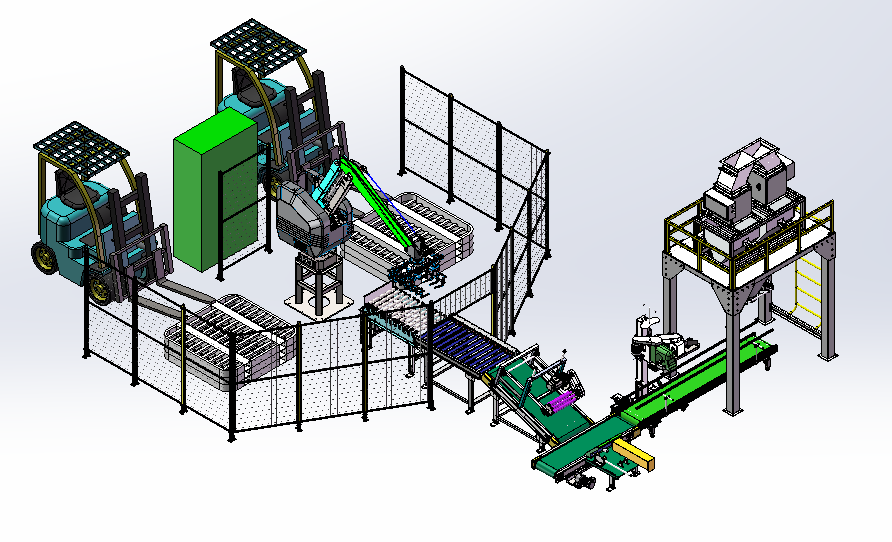
Robotic Arms Redefine Panel Production Efficiency
How Robotic Arm is Reshaping the Future of Woodworking
In the global woodworking industry, the demand for precision, speed, and sustainability continues to rise. As manufacturers face mounting pressure to reduce costs, meet eco-friendly standards, and scale production, robotic arms have emerged as a transformative solution. By automating critical processes—from material handling to quality control—these intelligent machines are redefining efficiency in panel production.
Key Applications Driving Industrial Transformation
1. Streamlined Material Handling
Robotic arms equipped with vacuum grippers or precision clamps handle everything from raw logs to finished veneer sheets with unmatched accuracy. For example:
In plywood factories, robotic arms automate log loading, veneer cutting, and glue application, reducing cycle times by up to 50%.
In furniture manufacturing, collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human operators to assemble complex components, improving accuracy to ±0.05mm.
2. Intelligent Palletizing Systems
Automated palletizing ensures flawless stacking while adapting to diverse requirements:
Dynamic load balancing: Robotic arms adjust stacking patterns in real time based on panel dimensions and weight.
High-speed throughput: Modern systems achieve 180–240 cycles per hour, cutting labor costs by up to 70%.
Space optimization: AI-driven algorithms maximize pallet density, reducing shipping costs by 20–30%.
3. AI-Powered Quality Assurance
When paired with machine vision and deep learning, robotic arms become relentless quality control agents:
Defect detection: Cameras and sensors identify cracks, knots, or warping at speeds exceeding human capability.
Automated sorting: Non-conforming panels are segregated in real time, ensuring 100% compliance with industry standards (e.g., FSC certification).
Edge trimming: Cobots guide panels through precision-cutting stations, minimizing waste and maximizing yield.
Technical Innovations Enhancing Competitiveness
a. Modular Tooling Systems
Robotic arms can be equipped with specialized end-effectors tailored to specific tasks:
Hybrid grippers: Combine suction cups and mechanical clamps for handling diverse materials (e.g., smooth veneer, textured engineered wood).
Heat-resistant coatings: Enable operation near kilns or ovens without compromising grip strength.
Antistatic modules: Prevent dust accumulation during resin-coated panel handling.
b. Industry 4.0 Integration
IoT connectivity: Real-time data sharing with ERP/MES systems optimizes workflow and predicts maintenance needs.
Predictive analytics: Machine learning algorithms detect tool wear or process inefficiencies before they escalate.
Digital twin technology: Simulate production scenarios to refine cycle times and energy consumption.
c. Sustainability-First Design
Energy efficiency: Regenerative braking systems reduce power consumption by 15–20%.
Emission control: Integrated filtration units capture volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during resin application.
Circular economy integration: Automated disassembly of scrap panels for recycling or biomass fuel conversion.
Global Impact: Success Stories from Diverse Industries
1. European Furniture Giant
A leading Italian furniture brand deployed UR10e cobots for cabinet assembly, achieving:
300% faster production cycles.
99.8% defect-free output.
€200,000 annual savings in labor and rework costs.
2. Southeast Asian Engineered Wood Plant
A Malaysian plywood manufacturer integrated robotic arms with IoT sensors, resulting in:
40% reduction in raw material waste.
25% lower energy bills.
Compliance with EU Ecolabel standards for sustainable production.
3. African Panel Producer
A Nigerian company adopted collaborative robots for custom door panel fabrication, overcoming challenges like:
Inconsistent raw material sizes.
High humidity environments.
Shortage of skilled labor.
The Road Ahead: Trends Shaping Robotic Automation
Swarm robotics: Coordination of multiple arms for large-scale, synchronized operations.
Edge computing: Onboard AI processing for real-time decision-making.
Hybrid automation: Combining robotic arms with AGVs for end-to-end material flow automation.
Conclusion
In an era where speed, precision, and sustainability define industrial success, robotic arms are no longer optional—they are essential. By automating material handling, quality control, and logistics, manufacturers can achieve unprecedented efficiency while meeting global demands for eco-friendly practices. As technologies like AI and IoT continue to evolve, the role of robotic arms in woodworking will only expand—ushering in a new era of smart, adaptive manufacturing. For suppliers and manufacturers seeking to stay ahead, investing in robotic automation isn’t just about cutting costs—it’s about future-proofing your business.